Building Real-Time Features with Firebase Cloud Messaging
Push notifications are one of the most powerful engagement tools in mobile development. A well-timed notification brings users back to your app, drives conversions, and keeps your product top of mind. Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM) is the industry standard for delivering push notifications and real-time data messages across iOS and Android.
This guide covers implementing FCM from setup through to advanced patterns like topic messaging, data payloads, and notification analytics.
FCM Architecture
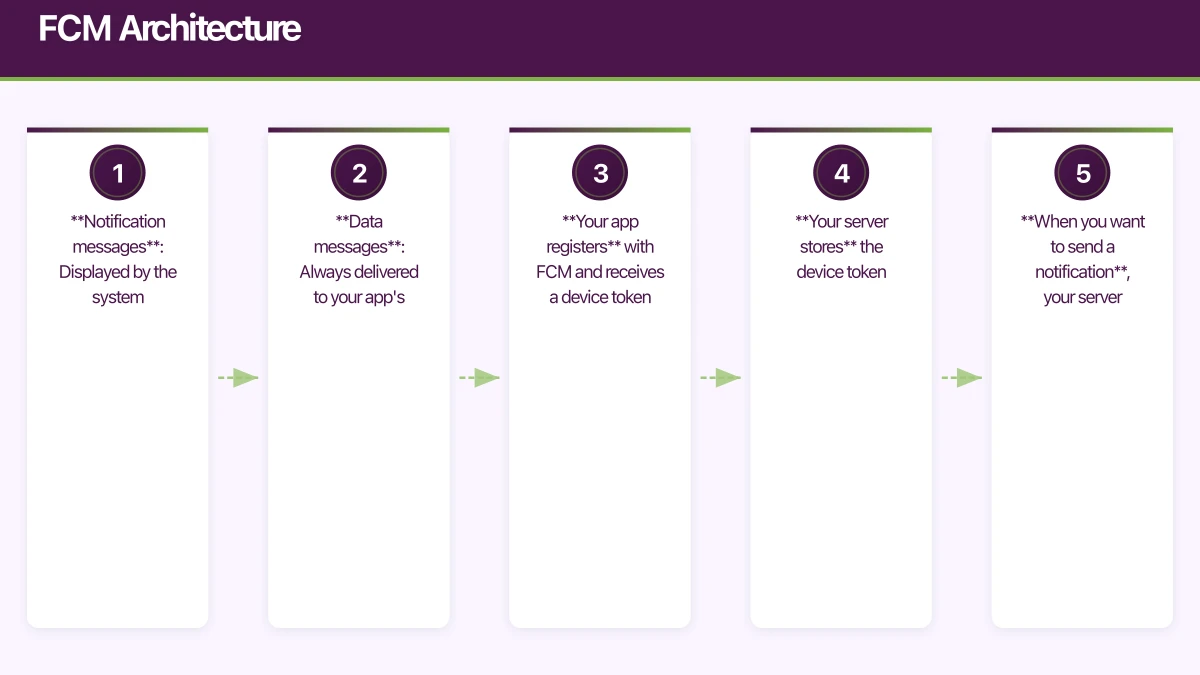
FCM operates on a simple model:
- Your app registers with FCM and receives a device token
- Your server stores the device token
- When you want to send a notification, your server sends a message to FCM with the target token
- FCM delivers the message to the device
FCM supports two types of messages:
- Notification messages: Displayed by the system automatically when the app is in the background. Handled by your app when in the foreground.
- Data messages: Always delivered to your app’s message handler. Your app decides what to do with the data.
iOS Setup

Configure APNs
FCM on iOS uses Apple Push Notification service (APNs) under the hood. You need an APNs authentication key or certificate.
- Generate an APNs key in your Apple Developer account
- Upload the key to the Firebase Console (Project Settings, Cloud Messaging, Apple app configuration)
App Configuration
import Firebase
import FirebaseMessaging
import UserNotifications
@main
class AppDelegate: UIResponder, UIApplicationDelegate, UNUserNotificationCenterDelegate, MessagingDelegate {
func application(
_ application: UIApplication,
didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplication.LaunchOptionsKey: Any]?
) -> Bool {
FirebaseApp.configure()
// Set delegates
UNUserNotificationCenter.current().delegate = self
Messaging.messaging().delegate = self
// Request notification permission
requestNotificationPermission()
// Register for remote notifications
application.registerForRemoteNotifications()
return true
}
private func requestNotificationPermission() {
UNUserNotificationCenter.current().requestAuthorization(
options: [.alert, .badge, .sound]
) { granted, error in
if granted {
print("Notification permission granted")
}
}
}
// FCM token received
func messaging(
_ messaging: Messaging,
didReceiveRegistrationToken fcmToken: String?
) {
guard let token = fcmToken else { return }
print("FCM Token: \(token)")
// Send token to your server
Task {
await sendTokenToServer(token)
}
}
// APNs token received
func application(
_ application: UIApplication,
didRegisterForRemoteNotificationsWithDeviceToken deviceToken: Data
) {
Messaging.messaging().apnsToken = deviceToken
}
// Foreground notification handling
func userNotificationCenter(
_ center: UNUserNotificationCenter,
willPresent notification: UNNotification,
withCompletionHandler completionHandler: @escaping (UNNotificationPresentationOptions) -> Void
) {
let userInfo = notification.request.content.userInfo
handleNotificationData(userInfo)
// Show the notification even when app is in foreground
completionHandler([.banner, .sound, .badge])
}
// Notification tap handling
func userNotificationCenter(
_ center: UNUserNotificationCenter,
didReceive response: UNNotificationResponse,
withCompletionHandler completionHandler: @escaping () -> Void
) {
let userInfo = response.notification.request.content.userInfo
handleNotificationTap(userInfo)
completionHandler()
}
private func handleNotificationData(_ userInfo: [AnyHashable: Any]) {
if let screen = userInfo["screen"] as? String {
NavigationManager.shared.navigate(to: screen)
}
}
}Android Setup
App Configura
 tion
tion
// AndroidManifest.xml
<service
android:name=".FCMService"
android:exported="false">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.google.firebase.MESSAGING_EVENT" />
</intent-filter>
</service>
{/* Default notification channel */}
<meta-data
android:name="com.google.firebase.messaging.default_notification_channel_id"
android:value="@string/default_notification_channel_id" />
{/* Default notification icon */}
<meta-data
android:name="com.google.firebase.messaging.default_notification_icon"
android:resource="@drawable/ic_notification" />
<meta-data
android:name="com.google.firebase.messaging.default_notification_color"
android:resource="@color/notification_color" />FCM Service
class FCMService : FirebaseMessagingService() {
override fun onNewToken(token: String) {
super.onNewToken(token)
// Send token to your server
sendTokenToServer(token)
}
override fun onMessageReceived(remoteMessage: RemoteMessage) {
super.onMessageReceived(remoteMessage)
// Handle data payload
if (remoteMessage.data.isNotEmpty()) {
handleDataMessage(remoteMessage.data)
}
// Handle notification payload (only received here when app is in foreground)
remoteMessage.notification?.let { notification ->
showNotification(
title = notification.title ?: "",
body = notification.body ?: "",
data = remoteMessage.data,
)
}
}
private fun handleDataMessage(data: Map<String, String>) {
val type = data["type"] ?: return
when (type) {
"chat_message" -> handleChatMessage(data)
"order_update" -> handleOrderUpdate(data)
"content_update" -> handleContentUpdate(data)
}
}
private fun showNotification(
title: String,
body: String,
data: Map<String, String>,
) {
val channelId = data["channel"] ?: "default"
val intent = createDeepLinkIntent(data)
val pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(
this, 0, intent,
PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT or PendingIntent.FLAG_IMMUTABLE
)
val notification = NotificationCompat.Builder(this, channelId)
.setSmallIcon(R.drawable.ic_notification)
.setContentTitle(title)
.setContentText(body)
.setAutoCancel(true)
.setContentIntent(pendingIntent)
.setPriority(NotificationCompat.PRIORITY_HIGH)
.build()
val manager = getSystemService(NOTIFICATION_SERVICE) as NotificationManager
manager.notify(System.currentTimeMillis().toInt(), notification)
}
}Notification Channels (Android 8+)
class NotificationChannelManager(private val context: Context) {
fun createChannels() {
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.O) {
val channels = listOf(
NotificationChannel(
"orders",
"Order Updates",
NotificationManager.IMPORTANCE_HIGH
).apply {
description = "Updates about your orders"
},
NotificationChannel(
"promotions",
"Promotions",
NotificationManager.IMPORTANCE_DEFAULT
).apply {
description = "Special offers and promotions"
},
NotificationChannel(
"chat",
"Messages",
NotificationManager.IMPORTANCE_HIGH
).apply {
description = "Chat messages and replies"
},
)
val manager = context.getSystemService(
Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE
) as NotificationManager
channels.forEach { manager.createNotificationChannel(it) }
}
}
}Server-Side: Sending Messages
Node.js with Firebase Admin SDK
const admin = require('firebase-admin');
admin.initializeApp({
credential: admin.credential.cert(serviceAccount),
});
// Send to a specific device
async function sendToDevice(token, title, body, data = {}) {
const message = {
token,
notification: { title, body },
data: Object.fromEntries(
Object.entries(data).map(([k, v]) => [k, String(v)])
),
android: {
priority: 'high',
notification: {
channelId: data.channel || 'default',
sound: 'default',
},
},
apns: {
payload: {
aps: {
sound: 'default',
badge: 1,
},
},
},
};
return admin.messaging().send(message);
}
// Send to a topic
async function sendToTopic(topic, title, body, data = {}) {
const message = {
topic,
notification: { title, body },
data: Object.fromEntries(
Object.entries(data).map(([k, v]) => [k, String(v)])
),
};
return admin.messaging().send(message);
}
// Send to multiple devices
async function sendToMultipleDevices(tokens, title, body, data = {}) {
const message = {
notification: { title, body },
data: Object.fromEntries(
Object.entries(data).map(([k, v]) => [k, String(v)])
),
tokens,
};
const response = await admin.messaging().sendMulticast(message);
// Handle failures
if (response.failureCount > 0) {
const failedTokens = [];
response.responses.forEach((resp, idx) => {
if (!resp.success) {
failedTokens.push(tokens[idx]);
}
});
await removeInvalidTokens(failedTokens);
}
}Topic Messaging
Topics let users subscribe to categories of notifications without your server needing to maintain subscription lists.
// iOS: Subscribe to topics
Messaging.messaging().subscribe(toTopic: "order_updates") { error in
if let error = error {
print("Subscribe error: \(error)")
}
}
// Unsubscribe
Messaging.messaging().unsubscribe(fromTopic: "promotions")// Android: Subscribe to topics
Firebase.messaging.subscribeToTopic("order_updates")
.addOnCompleteListener { task ->
if (task.isSuccessful) {
// Subscribed
}
}Topic Use Cases
- order_updates: All users who want order status notifications
- new_features: Users interested in product updates
- region_sydney: Location-based notifications for Sydney users
- premium_users: Notifications only for premium subscribers
Notification Analytics
Track notification effectiveness:
// Track when a notification is received
func handleNotificationReceived(_ userInfo: [AnyHashable: Any]) {
if let notificationId = userInfo["notification_id"] as? String {
Analytics.logEvent("notification_received", parameters: [
"notification_id": notificationId,
"type": userInfo["type"] as? String ?? "unknown",
])
}
}
// Track when a notification is tapped
func handleNotificationTap(_ userInfo: [AnyHashable: Any]) {
if let notificationId = userInfo["notification_id"] as? String {
Analytics.logEvent("notification_opened", parameters: [
"notification_id": notificationId,
"type": userInfo["type"] as? String ?? "unknown",
])
}
}Best Practices
Timing
- Respect time zones: Send notifications during waking hours in the user’s local timezone
- Do not spam: More than one notification per day causes opt-outs
- Batch non-urgent updates: Group multiple updates into a single summary notification
Content
- Be specific: “Your order has shipped” is better than “You have an update”
- Be actionable: Every notification should have a clear action the user can take
- Personalise: Use the user’s name and relevant context
Technical
- Handle token rotation: FCM tokens change. Always update your server when you receive a new token
- Remove stale tokens: When sends fail with “not registered”, remove the token from your database
- Use data messages for background processing: Notification messages may not wake your app on Android. Data messages always do.
- Test on real devices: Notification behaviour varies between simulators and real hardware
Conclusion
Firebase Cloud Messaging provides a reliable, free infrastructure for push notifications across iOS and Android. The key is using it thoughtfully: send relevant, timely notifications that provide genuine value, and track their effectiveness to continuously improve.
A well-executed notification strategy drives retention and engagement. A poorly executed one drives uninstalls.
For help building real-time notification systems for your mobile app, contact eawesome. We implement push notification strategies for Australian mobile applications.