Introduction
Deep linking is the invisible infrastructure that connects your marketing campaigns, user sharing, and onboarding flows. When implemented correctly, users click a link and land exactly where they need to be—whether they’re opening your app for the first time or the hundredth.
In September 2024, deep linking isn’t optional for serious mobile apps. Every marketing email, every social media campaign, every referral link depends on deep linking to track attribution and deliver seamless user experiences. Get it wrong, and you’re sending users to your app’s home screen, losing context, and missing attribution data. Get it right, and you’ve built a frictionless path from discovery to conversion.
This guide covers everything you need to implement production-ready deep linking: universal links for iOS, app links for Android, deferred deep linking for new users, attribution tracking, and the inevitable debugging challenges you’ll face. We’ll focus on real-world implementation patterns that work across React Native and native apps, with special attention to Australian market considerations.
Why Deep Linking Matters for Your App
The User Experience Problem
Without deep linking, every link click follows this frustrating path:
- User clicks promotional link → App opens
- App shows home screen
- User manually navigates to intended content (if they remember what they clicked)
- Conversion opportunity lost
With proper deep linking:
- User clicks promotional link → App opens directly to relevant content
- User completes intended action
- Attribution tracked correctly
- Conversion rates improve 30-50%
The Attribution Problem
Marketing campaigns without deep linking attribution are flying blind. You’re spending money on user acquisition without knowing which channels drive actual in-app behavior. Deep linking solves this by:
- Tracking which campaign brought users to your app
- Measuring conversion from click to in-app action
- Attributing revenue to specific marketing efforts
- Optimizing spend based on actual performance data
For Australian apps especially, where marketing budgets are often smaller and competition is fierce, attribution accuracy directly impacts sustainability.
The Technical Reality
Modern deep linking requires three complementary systems:
URI Schemes: Simple but limited
- Custom URLs like
yourapp://product/123 - Work only when app is installed
- No fallback to web
- Easiest to implement
Universal Links (iOS) / App Links (Android): Production standard
- HTTPS URLs like
https://yourapp.com.au/product/123 - Seamless fallback to website
- Better security and user trust
- Require server configuration
Deferred Deep Links: New user acquisition
- Preserve link context through app installation
- Critical for paid acquisition campaigns
- Require third-party service or custom implementation
Implementing URI Schemes: The Found
 ation
ation
URI schemes are the simplest deep linking method. While not production-ready on their own, they’re essential for handling app-to-app communication and serve as your fallback mechanism.
iOS URI Scheme Setup
1. Register Your URL Scheme
In Xcode, select your target → Info → URL Types → Add new URL Type:
- Identifier:
com.yourcompany.yourapp - URL Schemes:
yourapp(must be unique) - Role: Editor
Alternatively, edit Info.plist directly:
<key>CFBundleURLTypes</key>
<array>
<dict>
<key>CFBundleURLSchemes</key>
<array>
<string>yourapp</string>
</array>
<key>CFBundleURLName</key>
<string>com.yourcompany.yourapp</string>
</dict>
</array>Important: Choose a unique scheme. Generic names like shop or app will conflict with other apps. Use your brand name or a variation: awesomeapp, yourcompany, etc.
2. Handle Incoming Links
For UIKit apps, implement in AppDelegate.swift:
func application(_ app: UIApplication,
open url: URL,
options: [UIApplication.OpenURLOptionsKey: Any] = [:]) -> Bool {
// Validate the URL scheme
guard url.scheme == "yourapp" else {
return false
}
// Parse URL components
guard let components = URLComponents(url: url, resolvingAgainstBaseURL: true) else {
return false
}
// Route based on host and path
switch components.host {
case "product":
if let productId = components.queryItems?.first(where: { $0.name == "id" })?.value {
navigateToProduct(id: productId)
return true
}
case "category":
if let category = components.queryItems?.first(where: { $0.name == "name" })?.value {
navigateToCategory(name: category)
return true
}
case "user":
if let userId = components.queryItems?.first(where: { $0.name == "id" })?.value {
navigateToProfile(userId: userId)
return true
}
default:
// Unknown route - navigate to home
navigateToHome()
}
return false
}For SwiftUI apps using the App protocol:
import SwiftUI
@main
struct YourApp: App {
@StateObject private var router = DeepLinkRouter()
var body: some Scene {
WindowGroup {
ContentView()
.environmentObject(router)
.onOpenURL { url in
handleDeepLink(url: url)
}
}
}
private func handleDeepLink(url: URL) {
guard url.scheme == "yourapp" else { return }
if let components = URLComponents(url: url, resolvingAgainstBaseURL: true) {
router.route(to: DeepLink(from: components))
}
}
}3. Test Your Implementation
# iOS Simulator
xcrun simctl openurl booted "yourapp://product?id=123"
# Physical device via Safari
# Navigate to yourapp://product?id=123 in SafariAndroid URI Scheme Setup
1. Define Intent Filters
In AndroidManifest.xml, add intent filters to your main activity:
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:exported="true"
android:launchMode="singleTask">
{/* Existing launcher intent */}
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
{/* Deep link intent filter for products */}
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<data
android:scheme="yourapp"
android:host="product" />
</intent-filter>
{/* Deep link intent filter for categories */}
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<data
android:scheme="yourapp"
android:host="category" />
</intent-filter>
{/* Deep link intent filter for user profiles */}
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<data
android:scheme="yourapp"
android:host="user" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>Important: android:launchMode="singleTask" ensures only one instance of your activity exists, preventing duplicate screens when handling deep links.
2. Handle Deep Links in Your Activity
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
// Handle initial intent
handleIntent(intent)
}
override fun onNewIntent(intent: Intent?) {
super.onNewIntent(intent)
// Handle new intent when activity is already running
intent?.let { handleIntent(it) }
}
private fun handleIntent(intent: Intent) {
val action = intent.action
val data = intent.data
// Only process VIEW intents with data
if (action == Intent.ACTION_VIEW && data != null) {
handleDeepLink(data)
}
}
private fun handleDeepLink(uri: Uri) {
when (uri.host) {
"product" -> {
val productId = uri.getQueryParameter("id")
if (productId != null) {
navigateToProduct(productId)
} else {
navigateToHome()
}
}
"category" -> {
val categoryName = uri.getQueryParameter("name")
if (categoryName != null) {
navigateToCategory(categoryName)
} else {
navigateToHome()
}
}
"user" -> {
val userId = uri.getQueryParameter("id")
if (userId != null) {
navigateToProfile(userId)
} else {
navigateToHome()
}
}
else -> {
// Unknown route - default to home
navigateToHome()
}
}
}
private fun navigateToProduct(productId: String) {
// Your navigation logic
val fragment = ProductDetailFragment.newInstance(productId)
supportFragmentManager.beginTransaction()
.replace(R.id.container, fragment)
.commit()
}
private fun navigateToCategory(category: String) {
// Your navigation logic
}
private fun navigateToProfile(userId: String) {
// Your navigation logic
}
private fun navigateToHome() {
// Default navigation
}
}3. Test Your Implementation
# Android emulator or physical device
adb shell am start -W -a android.intent.action.VIEW -d "yourapp://product?id=123" com.yourcompany.yourapp
# Or create a test HTML file and open in Chrome
# <a href="yourapp://product?id=123">Test Deep Link</a>Universal Links (iOS): Production-Ready
 Implementation
Implementation
Universal Links are Apple’s solution for seamless deep linking using standard HTTPS URLs. When configured correctly, tapping https://yourapp.com.au/product/123 opens your app if installed, or your website if not.
Why Universal Links Matter
Security: Apple verifies domain ownership via HTTPS, preventing URL hijacking
User Trust: HTTPS URLs look legitimate compared to custom schemes
SEO Benefits: Same URLs work for web and app, improving search rankings
Fallback: Graceful degradation to website when app isn’t installed
Implementation Steps
1. Configure Apple App Site Association (AASA) File
Create apple-app-site-association (no file extension) and host it at:
https://yourapp.com.au/.well-known/apple-app-site-association
{
"applinks": {
"apps": [],
"details": [
{
"appID": "TEAMID.com.yourcompany.yourapp",
"paths": [
"/product/*",
"/category/*",
"/user/*",
"/promo/*",
"NOT /admin/*",
"NOT /api/*"
]
}
]
}
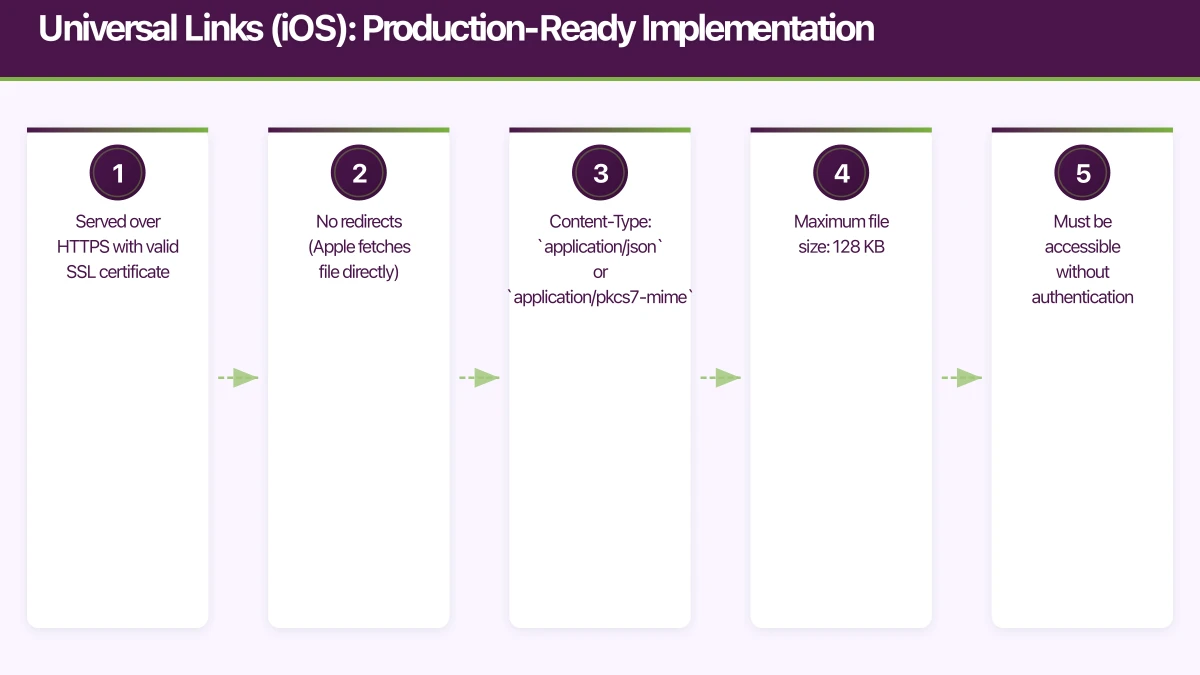
}Critical requirements:
- Served over HTTPS with valid SSL certificate
- No redirects (Apple fetches file directly)
- Content-Type:
application/jsonorapplication/pkcs7-mime - Maximum file size: 128 KB
- Must be accessible without authentication
Finding your Team ID and Bundle ID:
# Team ID: Found in Apple Developer account
# Or in Xcode: Select project → Signing & Capabilities → Team
# Bundle ID: Found in Xcode → General → Identity → Bundle Identifier
# Format: com.yourcompany.yourapp
# AppID format: TEAMID.BUNDLEIDTesting AASA file accessibility:
# Verify file is accessible
curl -I https://yourapp.com.au/.well-known/apple-app-site-association
# Should return 200 OK
# Content-Type: application/json
# Validate AASA file
# Apple's CDN caches your file here:
# https://app-site-association.cdn-apple.com/a/v1/yourapp.com.au2. Configure Your iOS App
In Xcode → Signing & Capabilities → Add Capability → Associated Domains:
applinks:yourapp.com.au
applinks:www.yourapp.com.auImportant: Don’t include https:// or trailing slashes. Just the domain.
3. Handle Universal Links in Your App
For UIKit apps, implement in AppDelegate.swift:
func application(_ application: UIApplication,
continue userActivity: NSUserActivity,
restorationHandler: @escaping ([UIUserActivityRestoring]?) -> Void) -> Bool {
// Only handle web browsing activities
guard userActivity.activityType == NSUserActivityTypeBrowsingWeb,
let url = userActivity.webpageURL else {
return false
}
return handleUniversalLink(url: url)
}
func handleUniversalLink(url: URL) -> Bool {
guard let components = URLComponents(url: url, resolvingAgainstBaseURL: true) else {
return false
}
// Parse path components
let pathComponents = components.path.split(separator: "/").map(String.init)
guard !pathComponents.isEmpty else {
navigateToHome()
return true
}
switch pathComponents[0] {
case "product":
if pathComponents.count > 1 {
let productId = pathComponents[1]
navigateToProduct(id: productId)
return true
}
case "category":
if pathComponents.count > 1 {
let categoryName = pathComponents[1]
navigateToCategory(name: categoryName)
return true
}
case "user":
if pathComponents.count > 1 {
let userId = pathComponents[1]
navigateToProfile(userId: userId)
return true
}
case "promo":
if let code = components.queryItems?.first(where: { $0.name == "code" })?.value {
applyPromoCode(code: code)
return true
}
default:
break
}
// If we can't handle the link, return false to open in Safari
return false
}For SwiftUI apps:
import SwiftUI
@main
struct YourApp: App {
@StateObject private var router = DeepLinkRouter()
var body: some Scene {
WindowGroup {
ContentView()
.environmentObject(router)
.onContinueUserActivity(NSUserActivityTypeBrowsingWeb) { userActivity in
if let url = userActivity.webpageURL {
handleUniversalLink(url: url)
}
}
}
}
private func handleUniversalLink(url: URL) {
if let deepLink = DeepLink.parse(from: url) {
router.route(to: deepLink)
}
}
}4. Test Universal Links
Critical: Universal Links only work when clicked from another app, not typed into Safari’s address bar or clicked from the same app.
Test methods:
# 1. Send yourself an email or iMessage with the link
# 2. Click the link - should open your app
# 3. Create a test webpage:
cat > test.html << 'EOF'
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head><title>Universal Link Test</title></head>
<body>
<h1>Test Universal Links</h1>
<a href="https://yourapp.com.au/product/123">Product 123</a><br>
<a href="https://yourapp.com.au/category/electronics">Electronics Category</a>
</body>
</html>
EOF
# 4. Host this file and open on device
# 5. Click links - should open your appDebugging Universal Links:
Long-press a link to see options. If you see “Open in [Your App]”, it’s configured correctly. If it always opens in Safari:
- Check AASA file is accessible at correct URL
- Verify Team ID and Bundle ID match exactly
- Confirm Associated Domains capability is enabled
- Check iOS 14+ Privacy settings: Settings → [Your App] → Universal Links
- Try deleting and reinstalling the app (AASA cache refresh)
App Links (Android): Production-Ready Implementation
App Links are Android’s equivalent to iOS Universal Links, providing verified HTTPS-based deep linking.
Implementation Steps
1. Generate Digital Asset Links File
First, get your app’s SHA-256 fingerprint:
# For debug keystore
keytool -list -v -keystore ~/.android/debug.keystore -alias androiddebugkey -storepass android -keypass android
# For release keystore
keytool -list -v -keystore /path/to/your-release-key.keystore -alias your-key-alias
# Look for SHA256 fingerprint like:
# 14:6D:E9:83:C5:73:06:50:D8:EE:B9:95:2F:34:FC:64:16:A0:83:42:E6:1D:BE:A8:8A:04:96:B2:3F:CF:44:E5Create assetlinks.json and host at:
https://yourapp.com.au/.well-known/assetlinks.json
[{
"relation": ["delegate_permission/common.handle_all_urls"],
"target": {
"namespace": "android_app",
"package_name": "com.yourcompany.yourapp",
"sha256_cert_fingerprints": [
"14:6D:E9:83:C5:73:06:50:D8:EE:B9:95:2F:34:FC:64:16:A0:83:42:E6:1D:BE:A8:8A:04:96:B2:3F:CF:44:E5"
]
}
}]Important: Include fingerprints for both debug and release builds during development:
"sha256_cert_fingerprints": [
"14:6D:E9:83:C5:73:06:50:D8:EE:B9:95:2F:34:FC:64:16:A0:83:42:E6:1D:BE:A8:8A:04:96:B2:3F:CF:44:E5",
"AB:CD:EF:12:34:56:78:90:AB:CD:EF:12:34:56:78:90:AB:CD:EF:12:34:56:78:90:AB:CD:EF:12:34:56:78:90"
]2. Configure Android Manifest
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:exported="true"
android:launchMode="singleTask">
{/* App Links for products */}
<intent-filter android:autoVerify="true">
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<data
android:scheme="https"
android:host="yourapp.com.au"
android:pathPrefix="/product" />
<data
android:scheme="https"
android:host="www.yourapp.com.au"
android:pathPrefix="/product" />
</intent-filter>
{/* App Links for categories */}
<intent-filter android:autoVerify="true">
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<data
android:scheme="https"
android:host="yourapp.com.au"
android:pathPrefix="/category" />
</intent-filter>
{/* App Links for user profiles */}
<intent-filter android:autoVerify="true">
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<data
android:scheme="https"
android:host="yourapp.com.au"
android:pathPrefix="/user" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>Key attribute: android:autoVerify="true" triggers automatic verification against your assetlinks.json file.
3. Handle App Links
The handling code is identical to URI schemes:
private fun handleDeepLink(uri: Uri) {
val pathSegments = uri.pathSegments
if (pathSegments.isEmpty()) {
navigateToHome()
return
}
when (pathSegments[0]) {
"product" -> {
if (pathSegments.size > 1) {
val productId = pathSegments[1]
navigateToProduct(productId)
} else {
navigateToHome()
}
}
"category" -> {
if (pathSegments.size > 1) {
val categoryName = pathSegments[1]
navigateToCategory(categoryName)
} else {
navigateToHome()
}
}
"user" -> {
if (pathSegments.size > 1) {
val userId = pathSegments[1]
navigateToProfile(userId)
} else {
navigateToHome()
}
}
"promo" -> {
val promoCode = uri.getQueryParameter("code")
if (promoCode != null) {
applyPromoCode(promoCode)
} else {
navigateToHome()
}
}
else -> navigateToHome()
}
}4. Test and Verify
# Test App Link
adb shell am start -W -a android.intent.action.VIEW -d "https://yourapp.com.au/product/123" com.yourcompany.yourapp
# Check verification status
adb shell pm get-app-links com.yourcompany.yourapp
# Expected output:
# com.yourcompany.yourapp:
# ID: <some-id>
# Signatures: [14:6D:E9:...]
# Domain verification state:
# yourapp.com.au: verified
# Manual verification (if needed)
adb shell pm verify-app-links --re-verify com.yourcompany.yourapp
# Reset verification state (useful during debugging)
adb shell pm set-app-links --package com.yourcompany.yourapp 0 allDebugging App Links:
If App Links aren’t working:
- Verify
assetlinks.jsonis accessible:curl https://yourapp.com.au/.well-known/assetlinks.json - Confirm SHA-256 fingerprint matches exactly (including colons)
- Check package name matches
applicationIdinbuild.gradle - Ensure
android:autoVerify="true"is present - Test on Android 6.0+ (App Links require Android M+)
Deferred Deep Linking: Handling New User Acquisition
Deferred deep linking is critical for paid acquisition campaigns. It preserves link context through the app installation process, ensuring users see the content they clicked on even if they had to install your app first.
The User Journey
Standard Deep Link (App Installed):
- User clicks link → App opens → Content displayed
Deferred Deep Link (App Not Installed):
- User clicks link → Redirected to App Store
- User installs app
- User opens app for first time
- App retrieves original link context
- Content displayed as if user had clicked while app was installed
Implementation Options
For September 2024, three main platforms dominate deferred deep linking:
Option 1: Branch.io (Recommended for Most Apps)
Pros:
- Comprehensive attribution tracking
- Free tier supports 10,000 monthly tracked users
- Easy integration with marketing platforms
- Australian data residency options available
- Excellent documentation
Cons:
- Paid plans required for scale (from USD $150/month)
- Third-party dependency
- Requires SDK integration
Implementation:
# Install Branch SDK
npm install react-native-branch --save
# or
# iOS: pod 'Branch'
# Android: implementation 'io.branch.sdk.android:library:5.+'// React Native implementation
import branch from 'react-native-branch';
// In your App.js
useEffect(() => {
// Subscribe to deep link events
const unsubscribe = branch.subscribe({
onOpenStart: ({uri, cachedInitialEvent}) => {
console.log('Branch link opened:', uri);
},
onOpenComplete: ({error, params, uri}) => {
if (error) {
console.error('Error from Branch:', error);
return;
}
// Handle deep link data
if (params['+clicked_branch_link']) {
// This is a Branch link
if (params.$deeplink_path) {
// Navigate to the path
navigateToPath(params.$deeplink_path);
}
// Track campaign attribution
if (params['~campaign']) {
analytics.track('campaign_attribution', {
campaign: params['~campaign'],
channel: params['~channel'],
feature: params['~feature']
});
}
}
}
});
return () => {
unsubscribe();
};
}, []);
// Create Branch links
async function createShareLink(productId) {
const branchUniversalObject = await branch.createBranchUniversalObject(
`product/${productId}`,
{
title: 'Amazing Product',
contentDescription: 'Check out this product!',
contentImageUrl: 'https://yourapp.com.au/images/product.jpg',
contentMetadata: {
customMetadata: {
product_id: productId,
category: 'electronics'
}
}
}
);
const linkProperties = {
feature: 'share',
channel: 'mobile_app'
};
const controlParams = {
$desktop_url: `https://yourapp.com.au/product/${productId}`,
$ios_url: `https://yourapp.com.au/product/${productId}`,
$android_url: `https://yourapp.com.au/product/${productId}`,
$deeplink_path: `product/${productId}`
};
const {url} = await branchUniversalObject.generateShortUrl(
linkProperties,
controlParams
);
return url; // Returns short URL like https://yourapp.app.link/abc123
}iOS Native:
import Branch
// In AppDelegate
func application(_ application: UIApplication,
didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplication.LaunchOptionsKey: Any]?) -> Bool {
Branch.getInstance().initSession(launchOptions: launchOptions) { params, error in
if let error = error {
print("Branch init error: \(error)")
return
}
guard let params = params as? [String: AnyObject] else { return }
// Check if this is a Branch link
if let clickedBranchLink = params["+clicked_branch_link"] as? Bool,
clickedBranchLink {
// Get deep link path
if let deepLinkPath = params["$deeplink_path"] as? String {
self.navigateToPath(path: deepLinkPath)
}
// Track attribution
if let campaign = params["~campaign"] as? String {
Analytics.shared.track("campaign_attribution", properties: [
"campaign": campaign,
"channel": params["~channel"] ?? "",
"feature": params["~feature"] ?? ""
])
}
}
}
return true
}Android Native:
import io.branch.referral.Branch
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onStart() {
super.onStart()
Branch.sessionBuilder(this).withCallback { branchUniversalObject, linkProperties, error ->
if (error != null) {
Log.e("Branch", "Init error: ${error.message}")
return@withCallback
}
linkProperties?.let { props ->
// Check if this is a Branch link
if (props.controlParams["+clicked_branch_link"] == "true") {
// Get deep link path
props.controlParams["\$deeplink_path"]?.let { path ->
navigateToPath(path)
}
// Track attribution
val campaign = props.controlParams["~campaign"]
if (campaign != null) {
Analytics.track("campaign_attribution", mapOf(
"campaign" to campaign,
"channel" to (props.controlParams["~channel"] ?: ""),
"feature" to (props.controlParams["~feature"] ?: "")
))
}
}
}
}.withData(intent.data).init()
}
}Option 2: Firebase Dynamic Links (Being Deprecated)
Important Update: Google announced Firebase Dynamic Links will be deprecated in August 2025. For new projects in September 2024, we recommend Branch or AppsFlyer instead.
If you’re already using Firebase Dynamic Links, plan migration before the August 2025 deadline.
Option 3: AppsFlyer OneLink
Pros:
- Enterprise-grade attribution platform
- Deep integration with advertising networks
- Advanced fraud prevention
- Popular among Australian gaming and e-commerce apps
Cons:
- Premium pricing (contact sales)
- More complex setup than Branch
- Overkill for simple apps
Implementation:
// React Native
import appsFlyer from 'react-native-appsflyer';
appsFlyer.initSdk({
devKey: 'YOUR_DEV_KEY',
isDebug: false,
appId: 'YOUR_APP_ID', // iOS only
onInstallConversionDataListener: true,
onDeepLinkListener: true
});
// Handle deep links
appsFlyer.onDeepLink(res => {
if (res?.deepLinkStatus === 'FOUND') {
const deepLinkValue = res.data.deep_link_value;
const campaign = res.data.campaign;
// Navigate based on deep link
navigateToPath(deepLinkValue);
// Track attribution
analytics.track('campaign_attribution', {
campaign: campaign,
media_source: res.data.media_source
});
}
});Choosing the Right Solution
Use Branch if:
- You need full-featured attribution on a budget
- You’re a startup or SME
- You want quick integration with minimal complexity
- Free tier (10,000 users/month) is sufficient
Use AppsFlyer if:
- You’re running significant paid acquisition campaigns (>$50K AUD/month)
- You need advanced fraud detection
- You require deep ad network integrations
- Enterprise support is critical
Build custom solution if:
- You have very specific attribution requirements
- You need complete data ownership
- You have engineering resources to maintain it
- Your app doesn’t require deferred deep linking
Building a Robust Deep Link Router
A centralized routing system makes deep link handling maintainable and testable.
Router Architecture
// DeepLink.ts - Define your deep link types
enum DeepLinkType {
Product = 'product',
Category = 'category',
User = 'user',
Promo = 'promo',
Search = 'search',
Unknown = 'unknown'
}
interface DeepLinkParams {
type: DeepLinkType;
id?: string;
params?: Record<string, string>;
}
class DeepLink {
readonly type: DeepLinkType;
readonly id?: string;
readonly params: Record<string, string>;
constructor(params: DeepLinkParams) {
this.type = params.type;
this.id = params.id;
this.params = params.params || {};
}
static parse(url: string): DeepLink {
try {
const urlObj = new URL(url);
const pathComponents = urlObj.pathname.split('/').filter(Boolean);
if (pathComponents.length === 0) {
return new DeepLink({ type: DeepLinkType.Unknown });
}
const type = pathComponents[0] as DeepLinkType;
const id = pathComponents[1];
// Parse query parameters
const params: Record<string, string> = {};
urlObj.searchParams.forEach((value, key) => {
params[key] = value;
});
return new DeepLink({ type, id, params });
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to parse deep link:', error);
return new DeepLink({ type: DeepLinkType.Unknown });
}
}
}
// DeepLinkRouter.ts - Handle navigation
class DeepLinkRouter {
private navigation: any; // Your navigation instance
constructor(navigation: any) {
this.navigation = navigation;
}
async route(deepLink: DeepLink): Promise<boolean> {
// Track deep link usage
analytics.track('deep_link_opened', {
type: deepLink.type,
id: deepLink.id,
params: deepLink.params
});
switch (deepLink.type) {
case DeepLinkType.Product:
return this.routeToProduct(deepLink);
case DeepLinkType.Category:
return this.routeToCategory(deepLink);
case DeepLinkType.User:
return this.routeToUser(deepLink);
case DeepLinkType.Promo:
return this.routeToPromo(deepLink);
case DeepLinkType.Search:
return this.routeToSearch(deepLink);
default:
return this.routeToHome();
}
}
private async routeToProduct(deepLink: DeepLink): Promise<boolean> {
if (!deepLink.id) {
return this.routeToHome();
}
try {
// Fetch product data to ensure it exists
const product = await api.getProduct(deepLink.id);
this.navigation.navigate('ProductDetail', {
productId: deepLink.id,
source: 'deep_link'
});
return true;
} catch (error) {
// Product not found - show error and navigate home
Alert.alert(
'Product Not Found',
'This product may no longer be available.',
[{ text: 'OK', onPress: () => this.routeToHome() }]
);
return false;
}
}
private async routeToCategory(deepLink: DeepLink): Promise<boolean> {
if (!deepLink.id) {
return this.routeToHome();
}
this.navigation.navigate('Category', {
categoryId: deepLink.id,
source: 'deep_link'
});
return true;
}
private async routeToUser(deepLink: DeepLink): Promise<boolean> {
if (!deepLink.id) {
return this.routeToHome();
}
// Check if user is authenticated
const isAuthenticated = await auth.isAuthenticated();
if (!isAuthenticated) {
// Save deep link for after authentication
await storage.save('pending_deep_link', deepLink);
this.navigation.navigate('Login', {
message: 'Please log in to view this profile',
redirect: true
});
return true;
}
this.navigation.navigate('Profile', {
userId: deepLink.id,
source: 'deep_link'
});
return true;
}
private async routeToPromo(deepLink: DeepLink): Promise<boolean> {
const promoCode = deepLink.params.code;
if (!promoCode) {
return this.routeToHome();
}
try {
// Validate and apply promo code
const result = await api.applyPromoCode(promoCode);
Alert.alert(
'Promo Code Applied!',
`You've saved ${result.discount}!`,
[{ text: 'Start Shopping', onPress: () => this.routeToHome() }]
);
return true;
} catch (error) {
Alert.alert(
'Invalid Promo Code',
'This promo code is not valid or has expired.',
[{ text: 'OK', onPress: () => this.routeToHome() }]
);
return false;
}
}
private async routeToSearch(deepLink: DeepLink): Promise<boolean> {
const query = deepLink.params.q;
if (!query) {
return this.routeToHome();
}
this.navigation.navigate('Search', {
query: query,
source: 'deep_link'
});
return true;
}
private routeToHome(): boolean {
this.navigation.navigate('Home');
return true;
}
}
export { DeepLink, DeepLinkRouter, DeepLinkType };Handling App State
Deep links arrive in different app states, requiring different handling strategies:
enum AppState {
NotRunning,
Background,
Foreground
}
class DeepLinkHandler {
private router: DeepLinkRouter;
async handleDeepLink(url: string, appState: AppState) {
const deepLink = DeepLink.parse(url);
switch (appState) {
case AppState.NotRunning:
// App launched from deep link
// Wait for app initialization before routing
await this.waitForAppReady();
await this.router.route(deepLink);
break;
case AppState.Background:
// App brought to foreground from deep link
// Safe to route immediately
await this.router.route(deepLink);
break;
case AppState.Foreground:
// Deep link opened while app active
// Ask user before navigating (they might be in the middle of something)
this.confirmNavigation(deepLink);
break;
}
}
private async waitForAppReady(): Promise<void> {
// Wait for critical initialization
await Promise.all([
auth.initialize(),
config.load(),
analytics.initialize()
]);
}
private confirmNavigation(deepLink: DeepLink): void {
Alert.alert(
'Open Link?',
'Would you like to view this content?',
[
{
text: 'Cancel',
style: 'cancel'
},
{
text: 'Open',
onPress: () => this.router.route(deepLink)
}
]
);
}
}Attribution Tracking for Australian Apps
Attribution tracking answers the crucial question: “Which marketing efforts actually drive app usage?”
What to Track
Essential attribution data:
-
Campaign Source: Where did the user come from?
- Facebook Ads
- Google Ads
- Email campaign
- Organic social media
- Referral link
-
Campaign Medium: What type of campaign?
- CPC (cost per click)
- Social
- Referral
-
Campaign Name: Specific campaign identifier
- “summer-sale-2024”
- “product-launch-sept”
- “referral-program”
-
User Journey: What happened after click?
- Time to first open
- Time to registration
- Time to first purchase
- Retention at Day 1, 7, 30
Implementing Attribution Tracking
// AttributionTracker.ts
interface AttributionData {
source: string;
medium: string;
campaign: string;
term?: string;
content?: string;
timestamp: number;
}
class AttributionTracker {
private static ATTRIBUTION_KEY = '@attribution_data';
private static ATTRIBUTION_WINDOW_DAYS = 30;
async trackAttribution(deepLink: DeepLink): Promise<void> {
const attribution: AttributionData = {
source: deepLink.params.utm_source || 'direct',
medium: deepLink.params.utm_medium || 'none',
campaign: deepLink.params.utm_campaign || 'none',
term: deepLink.params.utm_term,
content: deepLink.params.utm_content,
timestamp: Date.now()
};
// Save attribution data
await AsyncStorage.setItem(
AttributionTracker.ATTRIBUTION_KEY,
JSON.stringify(attribution)
);
// Send to analytics
analytics.identify({
acquisition_source: attribution.source,
acquisition_medium: attribution.medium,
acquisition_campaign: attribution.campaign
});
// Track initial attribution event
analytics.track('user_attributed', attribution);
}
async getAttribution(): Promise<AttributionData | null> {
const data = await AsyncStorage.getItem(AttributionTracker.ATTRIBUTION_KEY);
if (!data) {
return null;
}
const attribution: AttributionData = JSON.parse(data);
// Check if attribution is still within window
const daysSinceAttribution =
(Date.now() - attribution.timestamp) / (1000 * 60 * 60 * 24);
if (daysSinceAttribution > AttributionTracker.ATTRIBUTION_WINDOW_DAYS) {
return null;
}
return attribution;
}
async trackConversion(eventName: string, revenue?: number): Promise<void> {
const attribution = await this.getAttribution();
if (!attribution) {
return;
}
// Track conversion event with attribution context
analytics.track(eventName, {
attribution_source: attribution.source,
attribution_medium: attribution.medium,
attribution_campaign: attribution.campaign,
days_since_attribution:
(Date.now() - attribution.timestamp) / (1000 * 60 * 60 * 24),
revenue: revenue
});
}
}
// Usage example
const attributionTracker = new AttributionTracker();
// When deep link opens
await attributionTracker.trackAttribution(deepLink);
// When user makes purchase
await attributionTracker.trackConversion('purchase', 49.99);
// When user completes signup
await attributionTracker.trackConversion('signup_complete');UTM Parameter Structure
For Australian marketing campaigns, use consistent UTM parameters:
Product launch campaign:
https://yourapp.com.au/product/123?utm_source=facebook&utm_medium=cpc&utm_campaign=sept-launch&utm_content=video-ad-1
Email campaign:
https://yourapp.com.au/promo?code=SAVE20&utm_source=newsletter&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=weekly-deals-sept12
Influencer campaign:
https://yourapp.com.au/product/456?utm_source=instagram&utm_medium=influencer&utm_campaign=tech-reviewer-sept&utm_content=reviewer-name
Referral program:
https://yourapp.com.au/signup?ref=USER123&utm_source=referral&utm_medium=app&utm_campaign=referral-programCommon Challenges and Solutions
Challenge 1: Deep Links Not Opening App
Symptoms:
- Links open in browser instead of app
- “Open in [App]” option doesn’t appear
- Users complain links don’t work
iOS Debugging:
# 1. Check AASA file is accessible
curl https://yourapp.com.au/.well-known/apple-app-site-association
# 2. Verify Apple's CDN cached it
curl https://app-site-association.cdn-apple.com/a/v1/yourapp.com.au
# 3. Check app's associated domains
xcrun simctl get_app_container booted com.yourcompany.yourapp
# 4. Enable diagnostic logging
# Settings → Developer → Universal Links → Enable Associated Domains DevelopmentCommon iOS fixes:
- Team ID mismatch: Verify AASA file uses correct Team ID
- HTTPS issues: Ensure valid SSL certificate with no redirects
- User disabled: Settings → [Your App] → Universal Links must be enabled
- Cache issue: Delete and reinstall app to refresh AASA cache
- Testing incorrectly: Don’t type URLs in Safari - must click from another app
Android Debugging:
# Check App Links verification status
adb shell pm get-app-links com.yourcompany.yourapp
# View detailed verification results
adb shell dumpsys package d
# Look for your package and check domain verification statusCommon Android fixes:
- Fingerprint mismatch: Verify SHA-256 in assetlinks.json matches keystore
- Package name mismatch: Ensure assetlinks.json package_name matches build.gradle applicationId
- Verification failed: Run
adb shell pm verify-app-links --re-verify com.yourcompany.yourapp - Android version: App Links require Android 6.0+
- Intent filter missing autoVerify: Add
android:autoVerify="true"
Challenge 2: Deep Link Data Not Preserved
Symptom: App opens but navigates to home screen instead of deep link target
Solution: Ensure deep link handling happens at the right time in app lifecycle
// React Native - Handle deep links after navigation is ready
import { useEffect, useState } from 'react';
import { Linking } from 'react-native';
function App() {
const [isNavigationReady, setIsNavigationReady] = useState(false);
const navigationRef = useRef(null);
useEffect(() => {
if (!isNavigationReady) {
return;
}
// Handle initial deep link (app launched from link)
Linking.getInitialURL().then(url => {
if (url) {
handleDeepLink(url);
}
});
// Handle deep links while app is running
const subscription = Linking.addEventListener('url', ({url}) => {
handleDeepLink(url);
});
return () => subscription.remove();
}, [isNavigationReady]);
return (
<NavigationContainer
ref={navigationRef}
onReady={() => setIsNavigationReady(true)}>
{/* Your navigation */}
</NavigationContainer>
);
}Challenge 3: Deferred Deep Links Not Working
Symptoms:
- New installs don’t navigate to deep link content
- Attribution lost after installation
Debugging checklist:
- SDK initialization timing: Initialize Branch/AppsFlyer before checking for deep links
- App Store privacy: iOS 14.5+ requires ATT permission for some attribution methods
- Link expiration: Some platforms expire install attribution after 2 hours
- Testing methodology: Clear app data between tests, use different devices
iOS ATT handling:
import AppTrackingTransparency
func requestTrackingPermission() {
if #available(iOS 14.5, *) {
ATTrackingManager.requestTrackingAuthorization { status in
switch status {
case .authorized:
// Tracking authorized - full attribution available
Branch.getInstance().enableTracking(true)
case .denied, .restricted, .notDetermined:
// Limited tracking - some attribution may not work
Branch.getInstance().enableTracking(false)
@unknown default:
break
}
}
}
}Challenge 4: Poor Attribution Data Quality
Symptoms:
- Most installs show as “direct” or “unknown”
- Campaign performance unclear
- Marketing ROI unmeasurable
Solutions:
- Always use UTM parameters in all marketing links
- Implement server-side tracking for critical conversions
- Use shortened links from attribution platform (not bit.ly or other generic shorteners)
- Test attribution flow before launching campaigns
- Document UTM conventions and enforce across marketing team
UTM validation middleware:
function validateDeepLink(url: string): boolean {
const urlObj = new URL(url);
const hasUtmSource = urlObj.searchParams.has('utm_source');
const hasUtmMedium = urlObj.searchParams.has('utm_medium');
const hasUtmCampaign = urlObj.searchParams.has('utm_campaign');
if (!hasUtmSource || !hasUtmMedium || !hasUtmCampaign) {
// Log warning for internal links missing UTM parameters
analytics.track('deep_link_missing_utm', {
url: url,
missing: {
utm_source: !hasUtmSource,
utm_medium: !hasUtmMedium,
utm_campaign: !hasUtmCampaign
}
});
return false;
}
return true;
}Production Checklist
Before launching deep linking in production:
Infrastructure:
- AASA file accessible at
https://yourdomain.com.au/.well-known/apple-app-site-association - assetlinks.json accessible at
https://yourdomain.com.au/.well-known/assetlinks.json - SSL certificate valid with no redirect chains
- CDN configured to serve verification files correctly
- Both www and non-www domains handled
iOS Configuration:
- Associated Domains capability enabled with correct domains
- Team ID and Bundle ID match AASA file exactly
- Universal Link handling implemented in AppDelegate
- Tested on physical device (not just simulator)
- Long-press on links shows “Open in [App]”
Android Configuration:
- SHA-256 fingerprint matches assetlinks.json
- Package name matches build.gradle applicationId
- android:autoVerify=“true” present in intent filters
- Verification status confirmed via adb
- Tested on Android 6.0+ devices
Deep Link Routing:
- Centralized router handles all deep link types
- Graceful fallbacks for invalid/expired links
- Error handling for network failures
- Loading states while fetching deep link content
- Authentication required paths redirect to login
Attribution:
- Attribution SDK initialized before checking for deep links
- UTM parameters captured and stored
- Conversion events tracked with attribution context
- iOS ATT permission handled appropriately
- Testing completed with actual ad campaigns
Analytics:
- Deep link opens tracked
- Attribution data sent to analytics platform
- Conversion events include attribution context
- Failed deep links logged for debugging
Documentation:
- URL structure documented for marketing team
- UTM parameter conventions established
- Deep link creation process documented
- Testing procedures documented
Conclusion
Deep linking is essential infrastructure for modern mobile apps. In September 2024, users expect seamless experiences from any entry point—email, social media, advertising, or direct sharing. Attribution tracking enables data-driven marketing decisions, critical for Australian apps competing in tight markets with limited budgets.
Start with universal links and app links for immediate value. Add deferred deep linking when you start paid acquisition campaigns. Build a robust routing system that handles edge cases gracefully. Track attribution religiously to understand what’s working.
The implementation requires coordination between mobile developers, backend engineers, and marketing teams. But once in place, deep linking becomes the connective tissue between your marketing efforts and actual user behavior—turning clicks into conversions and campaigns into measurable ROI.
For Australian apps specifically, deep linking enables:
- Targeted regional campaigns with accurate attribution
- Viral growth through seamless sharing
- Retention campaigns that bring users back to specific content
- Performance marketing that tracks every dollar spent
Get it right, and you’ve built infrastructure that compounds in value as your app grows. Get it wrong, and you’re losing users and attribution data with every campaign. The time invested in proper implementation pays dividends for the life of your app.