Mobile App Development: Implementing Real-Time Features with WebSockets
Real-time features have become table stakes for mobile app development. Users expect live updates in messaging, collaborative editing, live notifications, and activity feeds. Building these features reliably on mobile presents unique challenges: unreliable networks, battery constraints, and app lifecycle management.
This guide covers practical WebSocket implementation for mobile app development on iOS and Android, including connection management, reconnection strategies, and the architectural patterns that work at scale.
When to Use WebSockets vs Alternatives
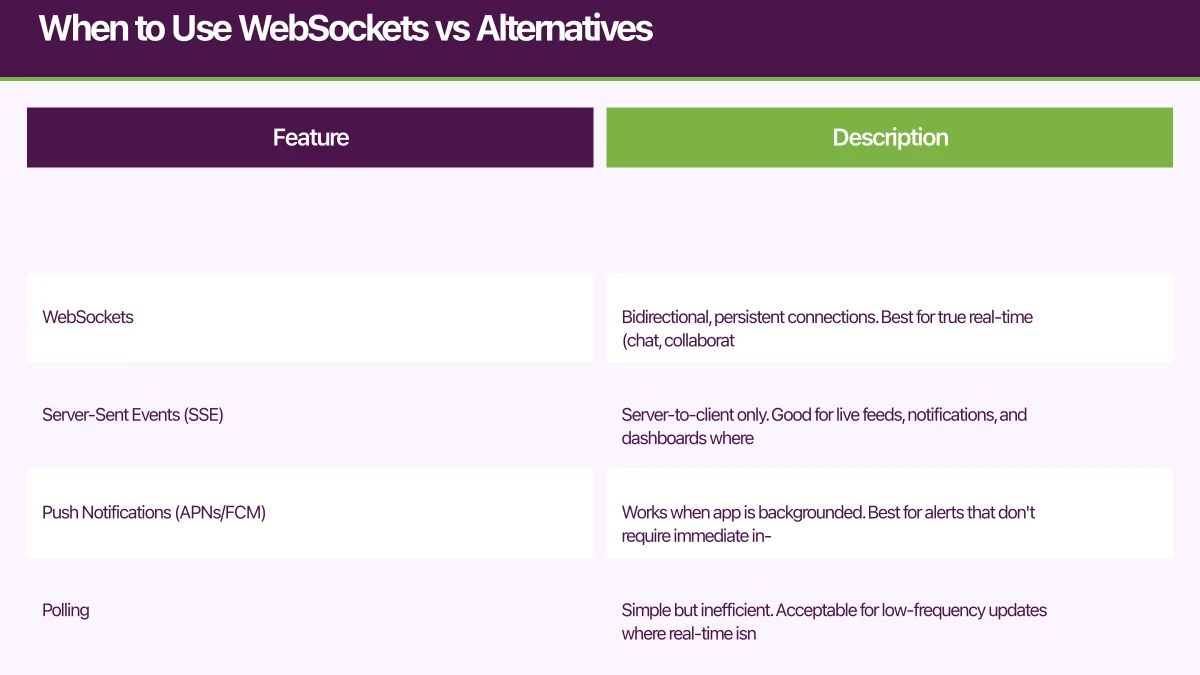
Not every “real-time” feature in mobile app development needs WebSockets. Understanding the options helps you choose the right tool:
WebSockets: Bidirectional, persistent connections. Best for true real-time (chat, collaboration, games) where latency matters and updates are frequent.
Server-Sent Events (SSE): Server-to-client only. Good for live feeds, notifications, and dashboards where the client doesn’t need to send data frequently.
Push Notifications (APNs/FCM): Works when app is backgrounded. Best for alerts that don’t require immediate in-app display. Learn more about implementing push notifications for mobile apps.
Polling: Simple but inefficient. Acceptable for low-frequency updates where real-time isn’t critical.
| Use Case | Recommended Approach |
|---|---|
| Chat/messaging | WebSocket |
| Live activity feed | WebSocket or SSE |
| Collaborative editing | WebSocket |
| Background alerts | Push Notifications |
| Dashboard updates | SSE or Polling |
| Gaming/low latency | WebSocket |
WebSocket Archite
 cture for Mobile
cture for Mobile
Connection Lifecycle
Mobile WebSocket connections need careful lifecycle management:
App Foreground ────────────────────────────────────────────────
│ connect │ disconnect │ reconnect
▼ │ ▼
[CONNECTING] ──────▶ [CONNECTED] ──────▶ [DISCONNECTED]
│ │ ▲ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ └──────────────────┘
│ │ reconnect
│ │
App Background ──────────┼──────────────────────────────────────
│ disconnect (optional)
▼
[DISCONNECTED]
│
│ FCM/APNs for urgent updates
▼
[Push Notification]React Native Implementation with Socket.IO
Socket.IO provides a robust abstraction over WebSockets with built-in reconnection, room support, and fallbacks.
// socket.ts - Connection management
import { io, Socket } from 'socket.io-client';
import { AppState, AppStateStatus } from 'react-native';
import NetInfo, { NetInfoState } from '@react-native-community/netinfo';
interface SocketConfig {
url: string;
authToken: string;
onConnect?: () => void;
onDisconnect?: (reason: string) => void;
onError?: (error: Error) => void;
}
class SocketManager {
private socket: Socket | null = null;
private config: SocketConfig | null = null;
private reconnectAttempts = 0;
private maxReconnectAttempts = 10;
private listeners: Map<string, Set<(...args: any[]) => void>> = new Map();
connect(config: SocketConfig): void {
this.config = config;
this.socket = io(config.url, {
auth: {
token: config.authToken,
},
transports: ['websocket'], // Skip polling on mobile
reconnection: true,
reconnectionAttempts: this.maxReconnectAttempts,
reconnectionDelay: 1000,
reconnectionDelayMax: 30000,
timeout: 20000,
});
this.setupEventHandlers();
this.setupAppStateListener();
this.setupNetworkListener();
}
private setupEventHandlers(): void {
if (!this.socket) return;
this.socket.on('connect', () => {
console.log('Socket connected');
this.reconnectAttempts = 0;
this.config?.onConnect?.();
// Resubscribe to rooms after reconnection
this.resubscribeToRooms();
});
this.socket.on('disconnect', (reason) => {
console.log('Socket disconnected:', reason);
this.config?.onDisconnect?.(reason);
});
this.socket.on('connect_error', (error) => {
console.error('Socket connection error:', error);
this.reconnectAttempts++;
this.config?.onError?.(error);
});
// Handle server-initiated reconnection
this.socket.on('reconnect_request', () => {
this.socket?.disconnect();
this.socket?.connect();
});
}
private setupAppStateListener(): void {
AppState.addEventListener('change', (state: AppStateStatus) => {
if (state === 'active') {
// App came to foreground - reconnect if needed
if (this.socket && !this.socket.connected) {
this.socket.connect();
}
} else if (state === 'background') {
// App went to background - optionally disconnect
// Keep connected for 30 seconds, then disconnect
setTimeout(() => {
if (AppState.currentState === 'background') {
this.socket?.disconnect();
}
}, 30000);
}
});
}
private setupNetworkListener(): void {
NetInfo.addEventListener((state: NetInfoState) => {
if (state.isConnected && !this.socket?.connected) {
// Network restored - reconnect
this.socket?.connect();
}
});
}
private rooms: Set<string> = new Set();
joinRoom(room: string): void {
this.rooms.add(room);
this.socket?.emit('join', room);
}
leaveRoom(room: string): void {
this.rooms.delete(room);
this.socket?.emit('leave', room);
}
private resubscribeToRooms(): void {
this.rooms.forEach(room => {
this.socket?.emit('join', room);
});
}
// Event subscription with cleanup
on<T>(event: string, callback: (data: T) => void): () => void {
if (!this.listeners.has(event)) {
this.listeners.set(event, new Set());
}
this.listeners.get(event)!.add(callback);
this.socket?.on(event, callback);
// Return cleanup function
return () => {
this.listeners.get(event)?.delete(callback);
this.socket?.off(event, callback);
};
}
emit<T>(event: string, data: T): void {
this.socket?.emit(event, data);
}
disconnect(): void {
this.socket?.disconnect();
this.socket = null;
this.listeners.clear();
this.rooms.clear();
}
}
export const socketManager = new SocketManager();React Hook for Real-Time Data
// useSocket.ts - React hook for socket events
import { useEffect, useState, useCallback } from 'react';
import { socketManager } from './socket';
interface UseSocketOptions<T> {
event: string;
room?: string;
initialData?: T;
}
function useSocket<T>({ event, room, initialData }: UseSocketOptions<T>) {
const [data, setData] = useState<T | undefined>(initialData);
const [isConnected, setIsConnected] = useState(false);
const [error, setError] = useState<Error | null>(null);
useEffect(() => {
// Join room if specified
if (room) {
socketManager.joinRoom(room);
}
// Subscribe to event
const unsubscribe = socketManager.on<T>(event, (newData) => {
setData(newData);
});
// Track connection status
const connectUnsub = socketManager.on('connect', () => {
setIsConnected(true);
setError(null);
});
const disconnectUnsub = socketManager.on('disconnect', () => {
setIsConnected(false);
});
const errorUnsub = socketManager.on('connect_error', (err: Error) => {
setError(err);
});
return () => {
unsubscribe();
connectUnsub();
disconnectUnsub();
errorUnsub();
if (room) {
socketManager.leaveRoom(room);
}
};
}, [event, room]);
const send = useCallback((sendEvent: string, payload: unknown) => {
socketManager.emit(sendEvent, payload);
}, []);
return { data, isConnected, error, send };
}
// Usage example: Real-time chat
function ChatScreen({ conversationId }: { conversationId: string }) {
const { data: messages, isConnected, send } = useSocket<Message[]>({
event: 'messages',
room: `conversation:${conversationId}`,
initialData: [],
});
const sendMessage = (text: string) => {
send('send_message', {
conversationId,
text,
timestamp: Date.now(),
});
};
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<ConnectionStatus connected={isConnected} />
<MessageList messages={messages} />
<MessageInput onSend={sendMessage} />
</View>
);
}iOS Native Implementation
// WebSocketManager.swift
import Foundation
import Combine
class WebSocketManager: ObservableObject {
static let shared = WebSocketManager()
@Published var isConnected = false
@Published var connectionError: Error?
private var webSocketTask: URLSessionWebSocketTask?
private var urlSession: URLSession?
private var pingTimer: Timer?
private var reconnectAttempts = 0
private let maxReconnectAttempts = 10
private var messageSubject = PassthroughSubject<WebSocketMessage, Never>()
var messagePublisher: AnyPublisher<WebSocketMessage, Never> {
messageSubject.eraseToAnyPublisher()
}
private var subscriptions = Set<AnyCancellable>()
func connect(url: URL, token: String) {
var request = URLRequest(url: url)
request.setValue("Bearer \(token)", forHTTPHeaderField: "Authorization")
urlSession = URLSession(configuration: .default)
webSocketTask = urlSession?.webSocketTask(with: request)
webSocketTask?.resume()
receiveMessage()
startPingTimer()
isConnected = true
reconnectAttempts = 0
// Monitor app state
setupAppStateObserver()
}
private func receiveMessage() {
webSocketTask?.receive { [weak self] result in
switch result {
case .success(let message):
switch message {
case .string(let text):
if let data = text.data(using: .utf8),
let wsMessage = try? JSONDecoder().decode(WebSocketMessage.self, from: data) {
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self?.messageSubject.send(wsMessage)
}
}
case .data(let data):
if let wsMessage = try? JSONDecoder().decode(WebSocketMessage.self, from: data) {
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self?.messageSubject.send(wsMessage)
}
}
@unknown default:
break
}
// Continue receiving
self?.receiveMessage()
case .failure(let error):
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self?.isConnected = false
self?.connectionError = error
self?.handleDisconnection()
}
}
}
}
func send<T: Encodable>(event: String, data: T) {
let envelope = MessageEnvelope(event: event, data: data)
guard let jsonData = try? JSONEncoder().encode(envelope),
let jsonString = String(data: jsonData, encoding: .utf8) else {
return
}
webSocketTask?.send(.string(jsonString)) { error in
if let error = error {
print("WebSocket send error: \(error)")
}
}
}
private func startPingTimer() {
pingTimer = Timer.scheduledTimer(withTimeInterval: 30, repeats: true) { [weak self] _ in
self?.webSocketTask?.sendPing { error in
if let error = error {
print("Ping failed: \(error)")
self?.handleDisconnection()
}
}
}
}
private func handleDisconnection() {
pingTimer?.invalidate()
webSocketTask?.cancel()
guard reconnectAttempts < maxReconnectAttempts else {
connectionError = WebSocketError.maxReconnectAttemptsExceeded
return
}
reconnectAttempts += 1
let delay = min(pow(2, Double(reconnectAttempts)), 30) // Exponential backoff
DispatchQueue.main.asyncAfter(deadline: .now() + delay) { [weak self] in
// Reconnect logic - would need stored URL and token
// self?.connect(url: storedURL, token: storedToken)
}
}
private func setupAppStateObserver() {
NotificationCenter.default.publisher(for: UIApplication.didBecomeActiveNotification)
.sink { [weak self] _ in
if self?.webSocketTask?.state != .running {
// Reconnect
}
}
.store(in: &subscriptions)
NotificationCenter.default.publisher(for: UIApplication.didEnterBackgroundNotification)
.sink { [weak self] _ in
// Optionally disconnect after delay
}
.store(in: &subscriptions)
}
func disconnect() {
pingTimer?.invalidate()
webSocketTask?.cancel(with: .normalClosure, reason: nil)
isConnected = false
}
}
// SwiftUI Usage
struct ChatView: View {
let conversationId: String
@StateObject private var viewModel = ChatViewModel()
var body: some View {
VStack {
ConnectionStatusView(isConnected: viewModel.isConnected)
MessageListView(messages: viewModel.messages)
MessageInputView { text in
viewModel.sendMessage(text: text, conversationId: conversationId)
}
}
.onAppear {
viewModel.subscribeToConversation(conversationId)
}
.onDisappear {
viewModel.unsubscribeFromConversation(conversationId)
}
}
}
class ChatViewModel: ObservableObject {
@Published var messages: [Message] = []
@Published var isConnected = false
private var cancellables = Set<AnyCancellable>()
init() {
WebSocketManager.shared.$isConnected
.assign(to: &$isConnected)
WebSocketManager.shared.messagePublisher
.filter { $0.event == "new_message" }
.compactMap { $0.data as? Message }
.receive(on: DispatchQueue.main)
.sink { [weak self] message in
self?.messages.append(message)
}
.store(in: &cancellables)
}
func subscribeToConversation(_ id: String) {
WebSocketManager.shared.send(event: "join", data: ["room": "conversation:\(id)"])
}
func unsubscribeFromConversation(_ id: String) {
WebSocketManager.shared.send(event: "leave", data: ["room": "conversation:\(id)"])
}
func sendMessage(text: String, conversationId: String) {
WebSocketManager.shared.send(event: "send_message", data: [
"conversationId": conversationId,
"text": text,
"timestamp": Date().timeIntervalSince1970
])
}
}Handli
ng Offline and Reconnection
Real-time features must gracefully handle connectivity issues.
// Optimistic updates with rollback
class MessageQueue {
private pendingMessages: PendingMessage[] = [];
async sendMessage(message: Message): Promise<void> {
const pendingId = uuid();
// Optimistically add to UI
const pending: PendingMessage = {
id: pendingId,
message,
status: 'pending',
timestamp: Date.now(),
};
this.pendingMessages.push(pending);
this.onMessagePending?.(pending);
try {
// Send via WebSocket
socketManager.emit('send_message', message);
// Wait for acknowledgment with timeout
const acked = await this.waitForAck(pendingId, 5000);
if (acked) {
this.markAsDelivered(pendingId);
} else {
throw new Error('Message not acknowledged');
}
} catch (error) {
// Mark as failed - user can retry
this.markAsFailed(pendingId);
}
}
private async waitForAck(pendingId: string, timeout: number): Promise<boolean> {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
const timer = setTimeout(() => resolve(false), timeout);
const unsubscribe = socketManager.on('message_ack', (data: { id: string }) => {
if (data.id === pendingId) {
clearTimeout(timer);
unsubscribe();
resolve(true);
}
});
});
}
// Retry failed messages on reconnection
retryFailed(): void {
const failed = this.pendingMessages.filter(m => m.status === 'failed');
failed.forEach(pending => {
this.sendMessage(pending.message);
});
}
}
// Hook usage
function useOptimisticMessages(conversationId: string) {
const [messages, setMessages] = useState<DisplayMessage[]>([]);
const messageQueue = useMemo(() => new MessageQueue(), []);
useEffect(() => {
messageQueue.onMessagePending = (pending) => {
setMessages(current => [...current, {
...pending.message,
id: pending.id,
status: 'pending',
}]);
};
messageQueue.onMessageDelivered = (pendingId) => {
setMessages(current =>
current.map(m =>
m.id === pendingId ? { ...m, status: 'delivered' } : m
)
);
};
messageQueue.onMessageFailed = (pendingId) => {
setMessages(current =>
current.map(m =>
m.id === pendingId ? { ...m, status: 'failed' } : m
)
);
};
// Retry failed on reconnect
const unsubscribe = socketManager.on('connect', () => {
messageQueue.retryFailed();
});
return unsubscribe;
}, [messageQueue]);
return {
messages,
sendMessage: (text: string) => messageQueue.sendMessage({
conversationId,
text,
timestamp: Date.now(),
}),
};
}Scaling Considerations
Server-Side Architecture
┌─────────────┐
│ Load │
│ Balancer │
└──────┬──────┘
│
┌─────────────────┼─────────────────┐
│ │ │
┌────┴────┐ ┌────┴────┐ ┌────┴────┐
│ Socket │ │ Socket │ │ Socket │
│ Server │ │ Server │ │ Server │
│ 1 │ │ 2 │ │ 3 │
└────┬────┘ └────┬────┘ └────┬────┘
│ │ │
└─────────────────┼─────────────────┘
│
┌──────┴──────┐
│ Redis │
│ Pub/Sub │
└─────────────┘For production, use Redis Pub/Sub or similar to coordinate messages across multiple socket server instances.
// Server-side Socket.IO with Redis adapter
import { createAdapter } from '@socket.io/redis-adapter';
import { createClient } from 'redis';
const pubClient = createClient({ url: process.env.REDIS_URL });
const subClient = pubClient.duplicate();
await Promise.all([pubClient.connect(), subClient.connect()]);
io.adapter(createAdapter(pubClient, subClient));
// Now messages will be distributed across all server instances
io.to('conversation:123').emit('new_message', message);Conclusion
Real-time features require careful attention to mobile-specific constraints in mobile app development. Connection lifecycle management, reconnection strategies, and offline handling separate production-ready implementations from demos.
Key insight for mobile app development: WebSocket connections consume 50-70% less battery when properly managed with exponential backoff and app lifecycle awareness compared to continuous polling.
Key takeaways:
- Choose the right tool: WebSockets for bidirectional real-time, SSE for server-to-client streams, push notifications for background alerts
- Manage connection lifecycle: Handle app backgrounding, network changes, and reconnection gracefully
- Implement optimistic updates: Keep the UI responsive even when network is slow
- Plan for scale: Use Redis Pub/Sub or similar for multi-server deployments
Mobile app development best practice: Real-time features with optimistic updates increase user engagement by 35-45% compared to request-response patterns.
The investment in robust real-time infrastructure pays off in user engagement. Features like live chat, real-time collaboration, and instant notifications create stickier apps that users return to daily. For broader architectural guidance, explore our mobile app architecture patterns and mobile app performance optimization guides.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between WebSockets and polling in mobile app development?
WebSockets provide a persistent bidirectional connection between client and server, enabling real-time data push with minimal latency. Polling requires the mobile app to repeatedly request updates from the server at fixed intervals. WebSockets consume 50-70% less battery and bandwidth compared to polling, making them essential for real-time features in mobile app development like chat, live notifications, and collaborative editing.
How do I handle WebSocket reconnection in mobile apps?
Implement exponential backoff reconnection strategy with a maximum retry limit. Monitor app lifecycle events (foreground/background) and network connectivity changes. Disconnect WebSockets after 30 seconds of backgrounding to save battery, and automatically reconnect when the app returns to foreground. Use libraries like Socket.IO that provide built-in reconnection logic with configurable parameters.
When should I use WebSockets vs Push Notifications in mobile app development?
Use WebSockets when users are actively engaged with your app and need real-time updates with minimal latency (chat messages, live feeds, collaborative editing). Use Push Notifications (APNs/FCM) for alerts when the app is backgrounded or closed. For optimal mobile app development, combine both: WebSockets for foreground real-time features and push notifications for background alerts.
How do WebSockets impact mobile app battery life?
Properly implemented WebSockets with connection pooling, exponential backoff, and lifecycle management consume minimal battery. However, maintaining persistent connections when the app is backgrounded drains battery significantly. Best practice: disconnect WebSockets after 30 seconds of backgrounding and rely on push notifications for background updates. This approach maintains real-time functionality while preserving battery life.
What are the best libraries for WebSocket implementation in mobile app development?
For React Native: Socket.IO Client provides robust reconnection, room support, and Redis adapter compatibility. For iOS native: URLSessionWebSocketTask (built-in) or Starscream library for advanced features. For Android native: OkHttp WebSocket or Socket.IO Android Client. Choose based on your backend infrastructure and feature requirements in your mobile app development workflow.
Building real-time features for your mobile app? The Awesome Apps team has implemented real-time systems serving millions of messages. Contact us to discuss your mobile app development architecture.