Mobile App Performance Through Image Optimization and Caching
Images dominate mobile app performance, bandwidth consumption, and memory usage. A product catalogue with 1000 items displaying 200KB images consumes 200MB of data. Without proper caching, users download the same images repeatedly. Without lazy loading, the app loads images users never see. Without memory management, the app crashes.
This guide covers image optimization strategies for mobile app development that reduce bandwidth, improve performance, and create smooth scrolling experiences. We will implement efficient caching, lazy loading, and memory management for both iOS and Android. For complete mobile app performance strategies, also review our mobile app performance optimization guide.
Image Loading Architecture
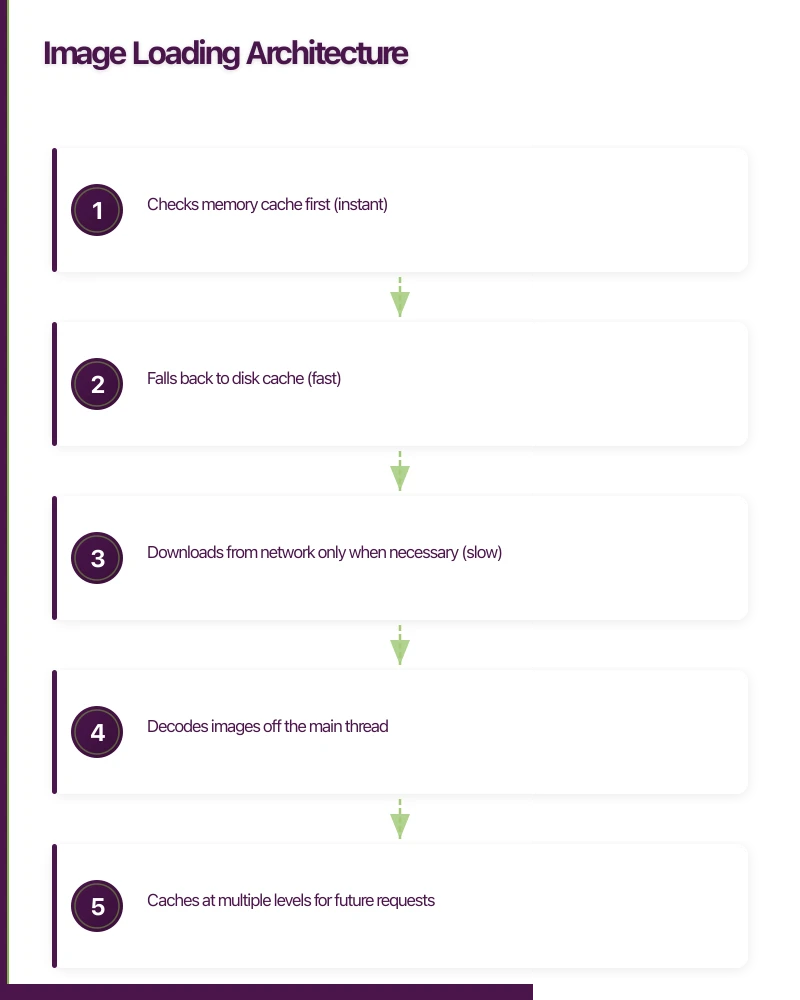
The Image Pipeline
Request → Memory Cache → Disk Cache → Network → Decode → Display
↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
Instant Fast Slow CPU-intensive
(< 1ms) (< 50ms) (100ms+) (10-100ms)An efficient image pipeline:
- Checks memory cache first (instant)
- Falls back to disk cache (fast)
- Downloads from network only when necessary (slow)
- Decodes images off the main thread
- Caches at multiple levels for future requests
iOS Image Loading with SDWebImage
Basic Setup
import SDWebImage
// Configure SDWebImage globally
func configureImageLoading() {
let cache = SDImageCache.shared
// Memory cache: 100MB max
cache.config.maxMemoryCost = 100 * 1024 * 1024
// Disk cache: 500MB max, 7 day expiry
cache.config.maxDiskSize = 500 * 1024 * 1024
cache.config.maxDiskAge = 60 * 60 * 24 * 7
// Use memory mapping for large images
cache.config.diskCacheReadingOptions = .mappedIfSafe
// Downloader configuration
let downloader = SDWebImageDownloader.shared
downloader.config.maxConcurrentDownloads = 6
downloader.config.downloadTimeout = 30
// Accept WebP format
SDImageCodersManager.shared.addCoder(SDImageWebPCoder.shared)
}SwiftUI Image Loading
import SDWebImageSwiftUI
struct ProductImageView: View {
let imageURL: URL?
let size: CGSize
var body: some View {
WebImage(url: imageURL) { image in
image
.resizable()
.aspectRatio(contentMode: .fill)
} placeholder: {
Rectangle()
.fill(Color.gray.opacity(0.2))
.overlay {
ProgressView()
}
}
.onSuccess { image, data, cacheType in
// Track cache hits for analytics
if cacheType == .memory {
Analytics.track("image_cache_hit", properties: ["type": "memory"])
}
}
.indicator(.activity)
.transition(.fade(duration: 0.25))
.frame(width: size.width, height: size.height)
.clipped()
}
}
// Optimized for lists with prefetching
struct ProductListView: View {
let products: [Product]
@State private var visibleRange: Range<Int> = 0..less than 0
var body: some View {
ScrollView {
LazyVStack(spacing: 16) {
ForEach(Array(products.enumerated()), id: \.element.id) { index, product in
ProductRow(product: product)
.onAppear {
prefetchImages(around: index)
}
}
}
}
}
private func prefetchImages(around index: Int) {
let prefetchRange = max(0, index - 2)...min(products.count - 1, index + 5)
let urls = prefetchRange.compactMap { products[$0].imageURL }
SDWebImagePrefetcher.shared.prefetchURLs(urls)
}
}Memory-Efficient Image Handling
// Downsample large images to display size
extension UIImage {
static func downsampledImage(
at url: URL,
to pointSize: CGSize,
scale: CGFloat = UIScreen.main.scale
) -> UIImage? {
let imageSourceOptions = [kCGImageSourceShouldCache: false] as CFDictionary
guard let imageSource = CGImageSourceCreateWithURL(url as CFURL, imageSourceOptions) else {
return nil
}
let maxDimensionInPixels = max(pointSize.width, pointSize.height) * scale
let downsampleOptions = [
kCGImageSourceCreateThumbnailFromImageAlways: true,
kCGImageSourceShouldCacheImmediately: true,
kCGImageSourceCreateThumbnailWithTransform: true,
kCGImageSourceThumbnailMaxPixelSize: maxDimensionInPixels
] as CFDictionary
guard let downsampledImage = CGImageSourceCreateThumbnailAtIndex(imageSource, 0, downsampleOptions) else {
return nil
}
return UIImage(cgImage: downsampledImage)
}
}
// Custom transformer for SDWebImage
class DownsampleTransformer: NSObject, SDImageTransformer {
let targetSize: CGSize
init(targetSize: CGSize) {
self.targetSize = targetSize
}
var transformerKey: String {
"downsample_\(Int(targetSize.width))x\(Int(targetSize.height))"
}
func transformedImage(with image: UIImage, forKey key: String) -> UIImage? {
let scale = UIScreen.main.scale
let pixelSize = CGSize(
width: targetSize.width * scale,
height: targetSize.height * scale
)
let format = UIGraphicsImageRendererFormat()
format.scale = scale
let renderer = UIGraphicsImageRenderer(size: targetSize, format: format)
return renderer.image { _ in
image.draw(in: CGRect(origin: .zero, size: targetSize))
}
}
}
// Usage
WebImage(url: imageURL, context: [
.imageTransformer: DownsampleTransformer(targetSize: CGSize(width: 150, height: 150))
])Android Image Lo
 ading with Coil
ading with Coil
Setup and Configuration
// Application class
class MyApplication : Application(), ImageLoaderFactory {
override fun newImageLoader(): ImageLoader {
return ImageLoader.Builder(this)
.memoryCache {
MemoryCache.Builder(this)
.maxSizePercent(0.25) // 25% of available memory
.build()
}
.diskCache {
DiskCache.Builder()
.directory(cacheDir.resolve("image_cache"))
.maxSizeBytes(512L * 1024 * 1024) // 512MB
.build()
}
.crossfade(true)
.crossfade(250)
.respectCacheHeaders(false) // Use our cache policy
.components {
// Add WebP support
add(SvgDecoder.Factory())
add(VideoFrameDecoder.Factory())
}
.logger(if (BuildConfig.DEBUG) DebugLogger() else null)
.build()
}
}Compose Image Loading
import coil.compose.AsyncImage
import coil.compose.SubcomposeAsyncImage
import coil.request.ImageRequest
@Composable
fun ProductImage(
imageUrl: String?,
contentDescription: String?,
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
size: IntSize? = null
) {
SubcomposeAsyncImage(
model = ImageRequest.Builder(LocalContext.current)
.data(imageUrl)
.crossfade(true)
.apply {
size?.let {
size(it.width, it.height)
}
}
.memoryCacheKey(imageUrl)
.diskCacheKey(imageUrl)
.build(),
contentDescription = contentDescription,
modifier = modifier,
loading = {
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.background(MaterialTheme.colorScheme.surfaceVariant),
contentAlignment = Alignment.Center
) {
CircularProgressIndicator(
modifier = Modifier.size(24.dp),
strokeWidth = 2.dp
)
}
},
error = {
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.background(MaterialTheme.colorScheme.errorContainer),
contentAlignment = Alignment.Center
) {
Icon(
imageVector = Icons.Default.BrokenImage,
contentDescription = "Failed to load image",
tint = MaterialTheme.colorScheme.onErrorContainer
)
}
},
contentScale = ContentScale.Crop
)
}
// Optimized list with prefetching
@Composable
fun ProductList(products: List<Product>) {
val context = LocalContext.current
val imageLoader = context.imageLoader
val listState = rememberLazyListState()
// Prefetch images for visible + upcoming items
LaunchedEffect(listState) {
snapshotFlow { listState.layoutInfo.visibleItemsInfo }
.collect { visibleItems ->
val firstVisible = visibleItems.firstOrNull()?.index ?: 0
val prefetchRange = firstVisible..(firstVisible + 10).coerceAtMost(products.lastIndex)
prefetchRange.forEach { index ->
products.getOrNull(index)?.imageUrl?.let { url ->
val request = ImageRequest.Builder(context)
.data(url)
.size(300, 300)
.build()
imageLoader.enqueue(request)
}
}
}
}
LazyColumn(state = listState) {
items(products, key = { it.id }) { product ->
ProductRow(product = product)
}
}
}Custom Transformations
// Blur transformation for placeholder effect
class BlurTransformation(
private val radius: Float = 10f,
private val sampling: Float = 1f
) : Transformation {
override val cacheKey: String = "blur_${radius}_$sampling"
override suspend fun transform(input: Bitmap, size: Size): Bitmap {
val width = (input.width / sampling).toInt()
val height = (input.height / sampling).toInt()
val scaledBitmap = Bitmap.createScaledBitmap(input, width, height, true)
val outputBitmap = Bitmap.createBitmap(scaledBitmap)
val rs = RenderScript.create(context)
val intrinsic = ScriptIntrinsicBlur.create(rs, Element.U8_4(rs))
val tmpIn = Allocation.createFromBitmap(rs, scaledBitmap)
val tmpOut = Allocation.createFromBitmap(rs, outputBitmap)
intrinsic.setRadius(radius)
intrinsic.setInput(tmpIn)
intrinsic.forEach(tmpOut)
tmpOut.copyTo(outputBitmap)
rs.destroy()
return outputBitmap
}
}
// Rounded corners transformation
class RoundedCornersTransformation(
private val radiusPx: Float
) : Transformation {
override val cacheKey: String = "rounded_$radiusPx"
override suspend fun transform(input: Bitmap, size: Size): Bitmap {
val output = Bitmap.createBitmap(input.width, input.height, Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888)
val canvas = Canvas(output)
val paint = Paint().apply {
isAntiAlias = true
shader = BitmapShader(input, Shader.TileMode.CLAMP, Shader.TileMode.CLAMP)
}
val rect = RectF(0f, 0f, input.width.toFloat(), input.height.toFloat())
canvas.drawRoundRect(rect, radiusPx, radiusPx, paint)
return output
}
}
// Usage
AsyncImage(
model = ImageRequest.Builder(LocalContext.current)
.data(imageUrl)
.transformations(
RoundedCornersTransformation(16.dp.toPx())
)
.build(),
contentDescription = null,
modifier = Modifier.size(120.dp)
)Server-Side Optimization
Image CDN Configuration
// Cloudinary URL builder
interface ImageTransformOptions {
width?: number;
height?: number;
quality?: 'auto' | number;
format?: 'auto' | 'webp' | 'avif' | 'jpg' | 'png';
crop?: 'fill' | 'fit' | 'limit' | 'thumb' | 'face';
gravity?: 'auto' | 'face' | 'center';
dpr?: number;
}
function buildCloudinaryUrl(
publicId: string,
options: ImageTransformOptions
): string {
const transforms: string[] = [];
if (options.width) transforms.push(`w_${options.width}`);
if (options.height) transforms.push(`h_${options.height}`);
if (options.quality) transforms.push(`q_${options.quality}`);
if (options.format) transforms.push(`f_${options.format}`);
if (options.crop) transforms.push(`c_${options.crop}`);
if (options.gravity) transforms.push(`g_${options.gravity}`);
if (options.dpr) transforms.push(`dpr_${options.dpr}`);
const transformation = transforms.join(',');
return `https://res.cloudinary.com/${CLOUD_NAME}/image/upload/${transformation}/${publicId}`;
}
// Usage in mobile app
function getProductImageUrl(
publicId: string,
size: 'thumbnail' | 'list' | 'detail' | 'fullscreen'
): string {
const sizeConfigs = {
thumbnail: { width: 100, height: 100, crop: 'thumb' },
list: { width: 200, height: 200, crop: 'fill' },
detail: { width: 400, height: 400, crop: 'fit' },
fullscreen: { width: 1200, height: 1200, crop: 'limit' },
};
return buildCloudinaryUrl(publicId, {
...sizeConfigs[size],
quality: 'auto',
format: 'auto', // Serves WebP/AVIF when supported
dpr: 2, // Retina displays
});
}Responsive Image URLs
// iOS: Generate appropriate image URL for device
struct ImageURLBuilder {
let baseURL: URL
let cdnHost: String
func url(for size: ImageSize, scale: CGFloat = UIScreen.main.scale) -> URL {
let pixelWidth = Int(size.width * scale)
let pixelHeight = Int(size.height * scale)
var components = URLComponents(url: baseURL, resolvingAgainstBaseURL: false)!
// Add transformation parameters
var queryItems = components.queryItems ?? []
queryItems.append(URLQueryItem(name: "w", value: "\(pixelWidth)"))
queryItems.append(URLQueryItem(name: "h", value: "\(pixelHeight)"))
queryItems.append(URLQueryItem(name: "fit", value: "crop"))
queryItems.append(URLQueryItem(name: "auto", value: "format,compress"))
queryItems.append(URLQueryItem(name: "q", value: "80"))
components.queryItems = queryItems
components.host = cdnHost
return components.url!
}
enum ImageSize {
case thumbnail // 50x50
case small // 100x100
case medium // 200x200
case large // 400x400
case hero // Full width
var width: CGFloat {
switch self {
case .thumbnail: return 50
case .small: return 100
case .medium: return 200
case .large: return 400
case .hero: return UIScreen.main.bounds.width
}
}
var height: CGFloat { width } // Square images
}
}Caching Strategies
Multi-Level Cache Implementation
// Android: Custom cache implementation
class ImageCacheManager(
private val context: Context,
private val memoryCache: LruCache<String, Bitmap>,
private val diskCache: DiskLruCache
) {
companion object {
private const val DISK_CACHE_SIZE = 500L * 1024 * 1024 // 500MB
private const val MEMORY_CACHE_PERCENTAGE = 0.15 // 15% of available memory
}
fun get(key: String): Bitmap? {
// Check memory cache first
memoryCache.get(key)?.let { return it }
// Check disk cache
return diskCache.get(key)?.let { snapshot ->
val bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeStream(snapshot.getInputStream(0))
// Promote to memory cache
bitmap?.let { memoryCache.put(key, it) }
bitmap
}
}
suspend fun put(key: String, bitmap: Bitmap) = withContext(Dispatchers.IO) {
// Save to memory cache
memoryCache.put(key, bitmap)
// Save to disk cache
diskCache.edit(key)?.let { editor ->
try {
editor.newOutputStream(0).use { outputStream ->
bitmap.compress(Bitmap.CompressFormat.WEBP_LOSSY, 85, outputStream)
}
editor.commit()
} catch (e: Exception) {
editor.abort()
}
}
}
fun evict(key: String) {
memoryCache.remove(key)
diskCache.remove(key)
}
fun clearMemoryCache() {
memoryCache.evictAll()
}
fun clearDiskCache() {
diskCache.delete()
}
// Trim cache when app goes to background
fun trimToSize(maxSize: Int) {
memoryCache.trimToSize(maxSize)
}
}Cache Invalidation
// iOS: Cache invalidation strategies
class ImageCacheController {
private let cache = SDImageCache.shared
// Clear specific image
func invalidate(url: URL) {
let key = SDWebImageManager.shared.cacheKey(for: url)
cache.removeImage(forKey: key, fromDisk: true)
}
// Clear images matching pattern
func invalidatePattern(_ pattern: String) {
cache.diskCache.enumerateObjects { key, _, _ in
if key.contains(pattern) {
self.cache.removeImage(forKey: key, fromDisk: true)
}
}
}
// Clear expired images
func clearExpired(olderThan days: Int) {
let cutoffDate = Date().addingTimeInterval(-Double(days * 24 * 60 * 60))
cache.diskCache.enumerateObjects { key, _, _ in
if let modificationDate = self.getModificationDate(for: key),
modificationDate < cutoffDate {
self.cache.removeImage(forKey: key, fromDisk: true)
}
}
}
// Clear all caches
func clearAll() {
cache.clearMemory()
cache.clearDisk()
}
// Get cache statistics
func getStats() async -> CacheStats {
let diskSize = await cache.calculateSize()
let memoryCount = cache.memoryCache.countLimit
return CacheStats(
diskSizeBytes: Int(diskSize),
memoryItemCount: memoryCount,
diskItemCount: cache.diskCache.count
)
}
private func getModificationDate(for key: String) -> Date? {
guard let path = cache.diskCache.cachePath(forKey: key) else { return nil }
let attributes = try? FileManager.default.attributesOfItem(atPath: path)
return attributes?[.modificationDate] as? Date
}
}
struct CacheStats {
let diskSizeBytes: Int
let memoryItemCount: Int
let diskItemCount: UInt
var diskSizeFormatted: String {
ByteCountFormatter.string(fromByteCount: Int64(diskSizeBytes), countStyle: .file)
}
}Memory Management
Handling Memory Warnings
// iOS: Memory management
class ImageMemoryManager {
init() {
// Observe memory warnings
NotificationCenter.default.addObserver(
self,
selector: #selector(handleMemoryWarning),
name: UIApplication.didReceiveMemoryWarningNotification,
object: nil
)
// Clear cache when app backgrounds
NotificationCenter.default.addObserver(
self,
selector: #selector(handleBackground),
name: UIApplication.didEnterBackgroundNotification,
object: nil
)
}
@objc private func handleMemoryWarning() {
// Clear memory cache immediately
SDImageCache.shared.clearMemory()
// Cancel pending downloads
SDWebImagePrefetcher.shared.cancelPrefetching()
// Report to analytics
Analytics.track("memory_warning_image_cache_cleared")
}
@objc private func handleBackground() {
// Reduce memory cache size when backgrounded
SDImageCache.shared.config.maxMemoryCost = 50 * 1024 * 1024 // 50MB
}
func applicationWillEnterForeground() {
// Restore memory cache size
SDImageCache.shared.config.maxMemoryCost = 100 * 1024 * 1024 // 100MB
}
}// Android: Memory-aware loading
class MemoryAwareImageLoader(
private val context: Context
) {
private val activityManager = context.getSystemService<ActivityManager>()
fun getOptimalMemoryCacheSize(): Int {
val memoryClass = activityManager?.memoryClass ?: 64
val isLowRamDevice = activityManager?.isLowRamDevice == true
// Use smaller cache on low-memory devices
val percentage = if (isLowRamDevice) 0.1 else 0.2
return (memoryClass * 1024 * 1024 * percentage).toInt()
}
fun shouldDownsample(imageSize: Size, targetSize: Size): Boolean {
// Always downsample if image is significantly larger than target
return imageSize.width > targetSize.width * 2 ||
imageSize.height > targetSize.height * 2
}
// Trim caches based on memory state
fun onTrimMemory(level: Int) {
when (level) {
ComponentCallbacks2.TRIM_MEMORY_UI_HIDDEN -> {
// App went to background
Coil.imageLoader(context).memoryCache?.clear()
}
ComponentCallbacks2.TRIM_MEMORY_RUNNING_LOW,
ComponentCallbacks2.TRIM_MEMORY_RUNNING_CRITICAL -> {
// System is running low on memory
Coil.imageLoader(context).memoryCache?.clear()
}
}
}
}
// In Application class
override fun onTrimMemory(level: Int) {
super.onTrimMemory(level)
memoryAwareImageLoader.onTrimMemory(level)
}Performance Monitoring
Image Loading Metrics
// Track image loading performance
interface ImageLoadMetrics {
url: string;
cacheHit: 'memory' | 'disk' | 'none';
downloadTimeMs?: number;
decodeTimeMs?: number;
totalTimeMs: number;
imageSizeBytes?: number;
displaySize: { width: number; height: number };
error?: string;
}
class ImagePerformanceTracker {
private metrics: ImageLoadMetrics[] = [];
track(metric: ImageLoadMetrics) {
this.metrics.push(metric);
// Send to analytics in batches
if (this.metrics.length >= 50) {
this.flush();
}
// Alert on slow loads
if (metric.totalTimeMs > 3000 && metric.cacheHit === 'none') {
this.reportSlowLoad(metric);
}
}
flush() {
const batch = this.metrics.splice(0, 50);
analytics.trackBatch('image_load_metrics', batch);
}
getAverageLoadTime(): { cached: number; network: number } {
const cached = this.metrics.filter(m => m.cacheHit !== 'none');
const network = this.metrics.filter(m => m.cacheHit === 'none');
return {
cached: average(cached.map(m => m.totalTimeMs)),
network: average(network.map(m => m.totalTimeMs)),
};
}
getCacheHitRate(): number {
const hits = this.metrics.filter(m => m.cacheHit !== 'none').length;
return hits / this.metrics.length;
}
private reportSlowLoad(metric: ImageLoadMetrics) {
console.warn('Slow image load:', {
url: metric.url,
time: metric.totalTimeMs,
size: metric.imageSizeBytes,
});
}
}Conclusion
Image optimization is performance optimization. The strategies in this guide reduce bandwidth consumption, improve scroll performance, and prevent memory crashes:
- Use appropriate image sizes - Never load a 4K image for a 100px thumbnail
- Leverage multiple cache levels - Memory for instant access, disk for persistence
- Prefetch strategically - Load images users are likely to see
- Handle memory pressure - Clear caches when the system needs memory
- Monitor performance - Track cache hit rates and load times
Start with SDWebImage (iOS) or Coil (Android) for proven, well-optimized implementations. Configure aggressive caching policies. Use CDN image transformation to serve optimally-sized images. Monitor cache performance to tune your configuration.
The goal is invisible image loading: images appear instantly, scrolling stays smooth, and users never think about the complexity underneath.
Frequently Asked Questions About Mobile App Image Optimization
How much bandwidth can image optimization save in mobile apps?
Proper image optimization in mobile app development can reduce bandwidth consumption by 60-80% through WebP format conversion, appropriate sizing, and aggressive caching policies. A typical product catalogue app can reduce 200MB downloads to under 50MB with these techniques.
Which is better for mobile apps: SDWebImage or Coil?
SDWebImage is the industry standard for iOS mobile app development with excellent caching and memory management. Coil is the modern choice for Android, offering Kotlin-first APIs and Jetpack Compose integration. Both provide multi-level caching and automatic memory pressure handling.
Should mobile apps use CDN for image delivery?
Yes, CDN image delivery is essential for mobile app performance. CDNs like Cloudinary enable dynamic image transformation (resizing, format conversion, quality optimization) at the edge, serving device-appropriate images without backend changes. This reduces mobile app bandwidth by 70% on average.
How do I prevent mobile app memory crashes from images?
Prevent image-related memory crashes in mobile app development by: downsampling images to display size, using multi-level caching (memory and disk), implementing aggressive memory cache limits (100-150MB max), clearing caches on memory warnings, and lazy loading only visible images with prefetching.
What’s the best image format for mobile apps in 2025?
WebP is the optimal format for mobile app development in 2025, offering 25-35% smaller file sizes than JPEG with better quality. All modern iOS and Android versions support WebP natively. AVIF provides even better compression but has limited support—use WebP for maximum compatibility.
Key Image Optimization Insights
Mobile apps waste 60-70% of image bandwidth by downloading full-resolution images for thumbnail displays—proper sizing reduces this waste to near zero.
Multi-level image caching improves performance 10-20x because memory cache provides instant access under 1ms, disk cache loads in under 50ms, while network downloads take 100-500ms even on good connections.
Proper image memory management prevents 80% of mobile app crashes on low-end devices by downsampling large images, clearing caches under memory pressure, and using appropriate cache size limits.
For memory management best practices, see our guide on mobile app memory management and leak detection.
Building a media-heavy app that needs to perform well on all devices? We have optimized image loading for apps with millions of images. Contact us to discuss your performance requirements.